Abstract
This paper presented the preparation of AgCu-SiO2 nanocomposite by green chemical reduction method combined with ultrasound. The physicochemical properties of AgCu-SiO2 were analyzed using techniques such as ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and atomic absorption spectroscopy. The analytical results indicated that the AgCu-SiO2 nanocomposite contained bimetallic nanoparticles of silver and copper, with sizes of 7.52 ± 1.12 nm. These nanoparticles were densely distributed on the silica surface. The antifungal activity of AgCu-SiO2 was compared to monometallic nanocomposites (Ag-SiO2, Cu-SiO2) and a commercial fungicide Ridomil gold 68 WG against Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium oxysporum and Pythium catenulatum, causing collar rots disease on Solanaceae. The results showed that AgCu-SiO2 exhibited good fungal growth inhibition compared to the monometallic nanocomposites. Specifically, the AgCu-SiO2 nanocomposite with complete fungal inhibition at a concentration of 125 ppm against all three studied fungal strains suggested its potential as an effective alternative to conventional chemical active ingredients in managing root rot disease.
MỞ ĐẦU
Bệnh lở cổ rễ của cây cà chua hay còn gọi là bệnh thối gốc cà chua, một trong những loại bệnh nguy hiểm, gây thiệt hại lớn trong sản xuất cà chua. Bệnh lở cổ rễ cà chua do nhóm các loại nấm có nguồn gốc trong đất gây ra, điển hình như nấm Rhizoctonia solani , Pythium sp., Fusarium sp. Bệnh lở cổ rễ lây lan trong môi trường nước và xâm nhập qua các vết thương cơ học, phát sinh, phát triển mạnh trong điều kiện độ ẩm cao hoặc mưa, nắng, rét, nóng thất thường 1 . Việc kiểm soát bệnh lở cổ rễ hiện nay chủ yếu tập trung vào sử dụng các thuốc diệt nấm phổ rộng hoặc một số chế phẩm sinh học từ nấm đối kháng, tuy nhiên hiệu quả chưa rõ rệt, đặc biệt vào mùa mưa, gây ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng đến năng suất và chất lượng cây trồng. Do đó, việc tìm kiếm các giải pháp mới để phòng trị bệnh lở cổ rễ của cây trở nên cấp thiết.
Công nghệ nano đang được nghiên cứu và ứng dụng để phòng trừ bệnh hại trên cây trồng 2 . Trong đó, nano bạc (Ag NP) được sử dụng phổ biến nhờ khả năng tiêu diệt nấm và vi khuẩn cây trồng rất hiệu quả, nó có thể kiểm soát được bệnh đạo ôn trên cây lúa do nấm Pyricularia oryzae gây ra 3 . Nano đồng (Cu NP) đã được sử dụng để phòng trừ vi khuẩn Ralstonia solanacearum gây bệnh héo xanh trên cây dưa chuột 4 . Mặc dù, cả Ag NP và Cu NP đều có đặc tính kháng vi sinh vật đáng kể, nhưng hỗn hợp Ag NP và Cu NP thể hiện đặc tính kháng kháng vi sinh vật lớn hơn so với từng Ag NP hoặc Cu NP riêng lẻ 5 , nhờ có tác dụng hiệp đồng của hai loại nano đối với vi sinh vật 6 , 7 . Đặc biệt, khi Ag NP và Cu NP được cố định trên những vật liệu mang như TiO 2 8 , khoáng chất aluminosilicate 9 , hiệu quả kháng vi sinh vật của vật liệu càng tăng lên, vì khi đó, các hạt nano Ag NP và Cu NP trở nên ổn định hơn, tránh bị kết tụ, kết đám lại.
Nano silica (Si NP), được sản xuất từ phụ phẩm tro trấu, chất đốt trong lò hơi công nghiệp ở Việt Nam, đang được ứng dụng đa dạng trong nhiều lĩnh vực sản xuất khác nhau như dược phẩm, cao su, sơn phủ và nông nghiệp 10 . Việc sản xuất nano silica được xem là một hướng phát triển năng lượng tái tạo vì vỏ trấu là nguồn sinh khối dồi dào, có thể tái tạo hằng năm từ các ruộng lúa nông nghiệp tại Việt Nam, đặc biệt tại vùng đồng bằng sông Cửu Long. Trong lĩnh vực trồng trọt, Si NP được sử dụng với nhiều công dụng khác nhau như khả năng chống ngộ độc do kim loại nặng 10 , khả năng chống chịu UVB 11 , khả năng chống chịu mặn 12 , khả năng chống mất nước 13 và khả năng dẫn truyền thuốc bảo vệ thực vật và phân bón 14 .
Bài báo trình bày sự kết hợp Ag NP, Cu NP và Si NP, tạo thành nanocomposite bạc, đồng trên nền silica (AgCu−SiO 2 ). Nanocomposite AgCu−SiO 2 được tổng hợp bằng phương pháp khử hóa học xanh kết hợp với sóng siêu âm và phân tích tính chất lý−hóa bằng các kỹ thuật phổ hấp thụ tử ngoại−khả kiến, giản đồ nhiễu xạ tia X, kính hiển vi điện tử quét và kính hiển vi điện tử truyền qua. Bên cạnh đó, hoạt tính kháng nấm của AgCu-SiO 2 được thực hiện đối với các nấm Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium oxysporum và Pythium catenulatum trong điều kiện phòng thí nghiệm.
VẬT LIỆU VÀ PHƯƠNG PHÁP
Hóa chất
Silica (SiO 2 , > 95%, kích thước từ 3−8 μm) được cung cấp bởi Công ty Cổ phần Công nghệ Nano BSB, Việt Nam); bạc nitrate (AgNO 3 , > 99%), đồng acetate ngậm một nước [Cu(CH 3 COO) 2 .H 2 O; 99,99%] được cung cấp bởi Sigma Aldrich. Sodium lauryl ether sulfate [CH 3 (CH 2 ) 11 (OCH 2 CH 2 ) n OSO 3 Na, 70%, Thái Lan], ascorbic acid (C 6 H 8 O 6 , > 99%, Xilong, Trung Quốc). Nước cất có độ dẫn điện < 5 μS/cm được sử dụng trong tất cả các thí nghiệm.
Phương pháp tổng hợp
Nanocomposite lưỡng kim bạc−đồng trên nền silica (AgCu-SiO 2 ) được tổng hợp bằng phương pháp khử hóa học xanh, kết hợp với sóng siêu âm cường độ cao. Cụ thể, hỗn hợp Cu(CH 3 COO) 2 .H 2 O và AgNO 3 có tỷ lệ mol 1:1 được khuấy từ trong 100 mL nước cất. Sau đó 0,2 gam silica và sodium lauryl ether sulfate (0,5 M) được thêm vào hỗn hợp hai muối. Sau 15 phút, ascorbic acid (0,5 g) được cho vào hỗn hợp và siêu âm hỗn hợp cường độ cao (HIELSCHER’S, 200W, 26 kHz) trong 15 phút; màu dung dịch chuyển từ màu trắng xanh sang đen xám. Tiếp theo, hỗn hợp được ly tâm ở 4000 vòng/phút trong 10 phút; sau đó, phần bột rắn được rửa với nước cất và ethanol (tỷ lệ 1:1) và sấy ở nhiệt độ 60 o C trong 8 giờ. Các mẫu Ag−SiO 2 và Cu−SiO 2 được tổng hợp bằng phương pháp tương tự để làm vật liệu đối chứng.
Phương pháp phân tích
Tính chất quang của vật liệu được xác định thông qua phổ hấp thụ từ ngoại – khả kiến (UV−Vis, Jasco V670) với khoảng bước sóng khảo sát từ 300–750 nm, tính chất tinh thể và thành phần pha được xác định bằng phương pháp nhiễu xạ tia X (XRD, D8 Advance-Bruker Eco) với bước sóng tia X phát ra từ nguồn Cu K α bằng 1,54 Å, khoảng ghi số liệu từ 10–80°, bước nhảy 0,0195°. Hàm lượng bạc trong các vật liệu được xác định bằng phép đo phổ nguồn plasma cảm ứng cao tần kết nối khối phổ (ICP-MS) trên máy iCAP-RQ ICP-MS, Thermo Scientific với đầu phun thạch anh đường kính 2,5 mm, skimmer cone bằng Ni, đường kính 3,5 mm, tốc độ phun mẫu 0,1843 L/phút, nguồn RF 1550 W và thời gian đo 60 giây. Hàm lượng đồng trong các vật liệu được xác định bằng phổ hấp thụ nguyên tử (AAS, AA-6800, Shimadzu) ở bước sóng 324,8 nm có dòng điện 6 mA, độ rộng khe 0,5 nm, thời gian đo 5 giây và tốc độ phun khí Air/C 2 H 2 là 2,5 L/phút.
Thử nghiệm hoạt tính kháng nấm
Khả năng kháng nấm của các vật liệu Ag−SiO 2 , Cu−SiO 2 , CuSiO 2 và AgCu−SiO 2 đối với các nấm Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium oxysporum và Pythium catenulatum được đánh giá bằng phương pháp nhiễm môi trường. Các mẫu nấm R. solani, F. oxysporum và P. catenulatum , gây bệnh lở cổ rễ cây được phân lập và cung cấp từ Bộ môn Bảo vệ Thực vật, Khoa Nông học, Trường Đại học Nông Lâm Tp. Hồ Chí Minh. Môi trường PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar gồm 200 g khoai tây, 20 g dextrose, 15 g agar cho 1 L môi trường) được khử trùng, bổ sung 20 μL hệ phân tán của các mẫu Ag−SiO 2 , Cu−SiO 2 và AgCu−SiO 2 trong nước cất (tương ứng với các hàm lượng kim loại trong hệ phân tán tính theo kết quả ICP-MS và AAS là 16, 32, 64, 125 ppm), và đổ vào đĩa petri với thể tích 10 mL/đĩa. Khoanh nấm (đường kính 0,5 cm) được đặt vào tâm đĩa petri, mặt nấm úp xuống mặt môi trường PDA, sau đó bọc đĩa bằng parafilm và ủ ở nhiệt độ 28 ± 2°C. Thuốc trừ bệnh thương mại Ridomil gold 68 WG với các hoạt chất metalaxyl-M (40 g/L) và mancozeb (640 g/L), đặc trị các nấm nói trên được sử dụng với tỷ lệ pha loãng khuyến cáo 300 g/100 lít nước (tương đương với nồng độ khuyến cáo 3000 ppm) để làm nghiệm thức đối chứng dương, và nước cất được sử dụng làm đối chứng âm. Thí nghiệm được thực hiện với mỗi nghiệm thức 5 lần lặp lại, mỗi lần lặp lại của một nghiệm thức là 1 đĩa petri.
Các chỉ tiêu theo dõi bao gồm đường kính trung bình của tản nấm, được xác định bởi công thức (1) và hiệu lực ức chế nấm của hoạt chất thuốc, được xác định theo công thức (2):
d = (d 1 + d 2 )/2 (1)
trong đó: d là đường kính trung bình tản nấm (tản sợi), còn d 1 và d 2 là chiều dài đường chéo của tản nấm (tản sợi).
H = (D - d)x100/D (2)
trong đó: H là hiệu lực ức chế nấm của hoạt chất thuốc, D là đường kính tản nấm của nghiệm thức đối chứng âm (mm), d là đường kính tản nấm của nghiệm thức chứa hoạt chất (mm).
KẾT QUẢ VÀ THẢO LUẬN
Tính chất vật liệu
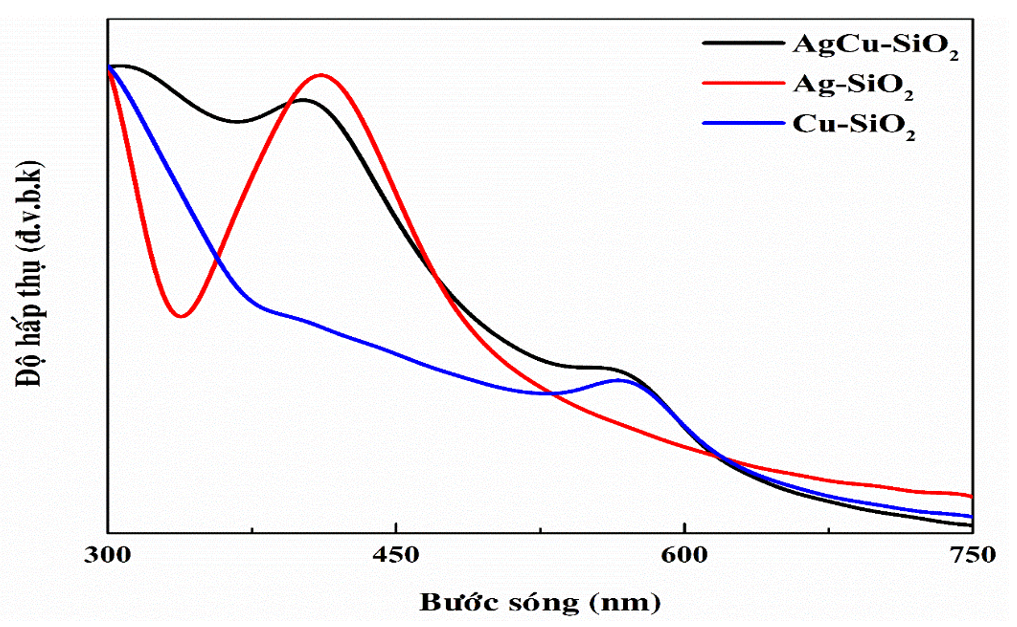
Figure 1 thể hiện phổ hấp thụ tử ngoại–khả kiến của các mẫu Ag−SiO 2 , Cu−SiO 2 và AgCu−SiO 2 . Các mẫu Ag−SiO 2 và Cu−SiO 2 thể hiện đỉnh hấp thụ đặc trưng cho dao động plasmon bề mặt của nano bạc và đồng lần lượt ở bước sóng 410 và 570 nm 15 , 16 . Mẫu AgCu−SiO 2 hiển thị hai đỉnh hấp thụ ở 403 và 568 nm, điều này thể hiện trong mẫu nanocomposite hình thành song song cả nano bạc và đồng ở trạng thái riêng lẻ hoặc tạo cấu trúc lưỡng kim bạc−đồng 17 , 18 .
Figure 1 . Phổ hấp thụ UV−Vis của các mẫu nanocomposite Ag−SiO2, Cu−SiO 2 và AgCu−SiO 2 .
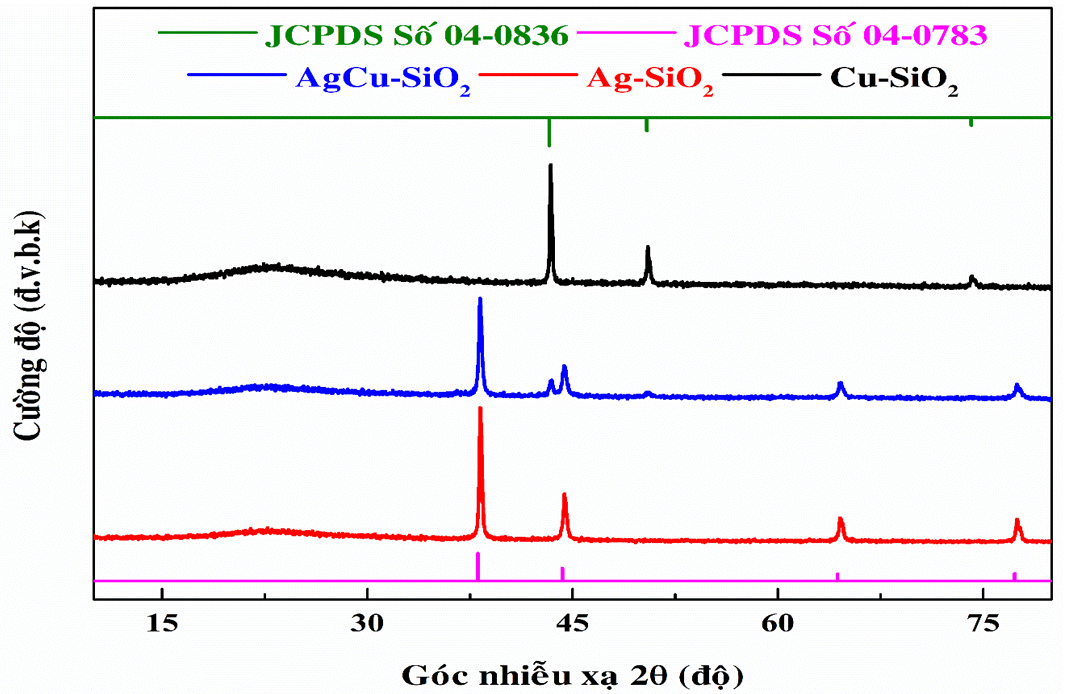
Figure 2 thể hiện giản đồ nhiễu xạ tia X các mẫu nanocomposite Ag−SiO 2 , Cu−SiO 2 và AgCu−SiO 2 . Kết quả XRD của các mẫu nanocomposite xuất hiện vùng nhiễu xạ rộng từ 15 đến 25°, được cho là vùng vô định hình của chất nền SiO 2 19 . Mẫu Cu−SiO 2 có xuất hiện 3 đỉnh nhiễu xạ tại vị trí góc 2θ lần lượt là 43,3°, 50,4° và 74,1° tương ứng với mặt (111), (200), (220) của mạng lập phương tâm mặt của kim loại đồng (JCPDS số 04-0836) 4 . Mẫu Ag−SiO 2 thể hiện rõ cấu trúc lập phương tâm mặt (FCC) của kim loại bạc theo JCPDS số 04-0783 với các đỉnh đặc trưng ở các vị trí 38,08°, 44,29°, 64,6° và 77,68°, tương ứng với các mặt phẳng tinh thể (111), (200), (220) và (311) 15 , 20 . Giản đồ XRD của AgCu−SiO 2 có tồn tại đồng thời các đỉnh nhiễu xạ, đặc trưng cho bạc, lẫn đồng. Điều này cho thấy AgCu−SiO 2 được tạo ra có cấu trúc composite lưỡng kim bạc−đồng 21 , 22 .
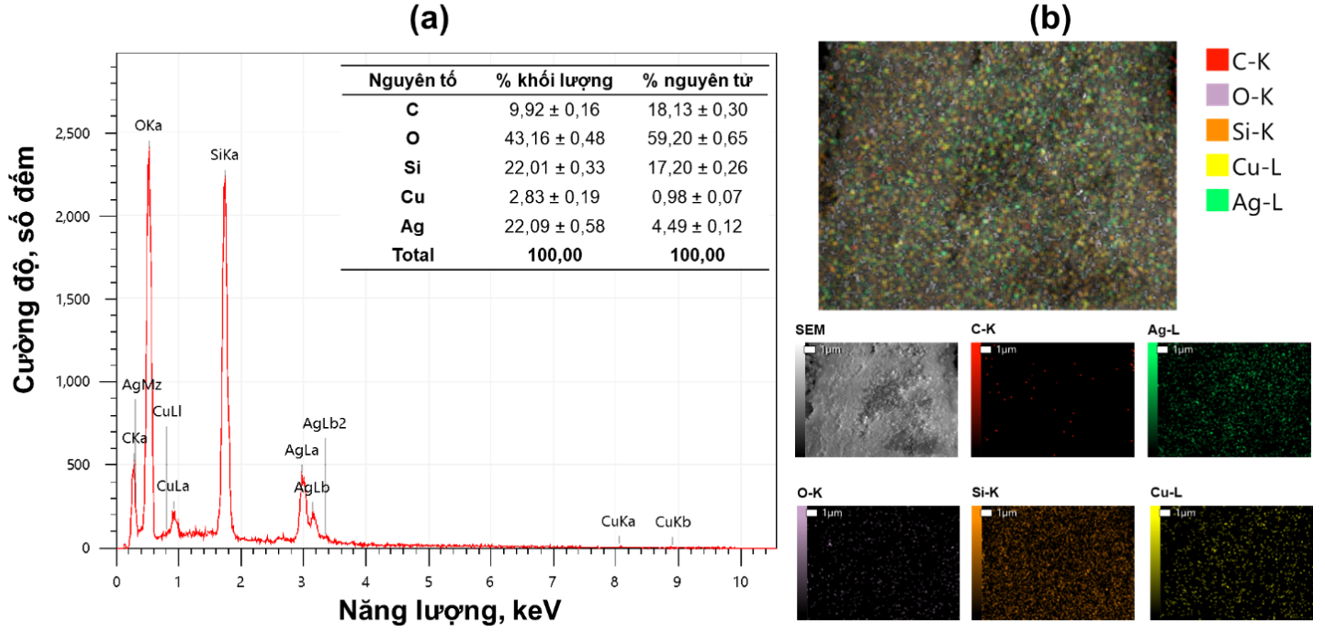
Figure 4 a trình bày kết quả phổ EDS của mẫu AgCu−SiO 2 , AgCu−SiO 2 chứa các nguyên tố silicium (22,01 ± 0,33% khối lượng), oxygen (43,16 ± 0,48% khối lượng), đồng (2,83 ± 0,19% khối lượng) và bạc (22,09 ± 0,58% khối lượng). Ngoài ra, trong mẫu AgCu−SiO 2 còn có sự hiện diện của carbon (9,92 ± 0,16% khối lượng), được quy cho sự tồn tại của một số chất hữu cơ, xuất phát từ các tiền chất sodium lauryl ether sulfate, ascorbic acid còn dư sau quá trình tổng hợp và băng keo carbon sử dụng để cố định mẫu AgCu−SiO 2 trong phép phân tích SEM-EDS.
Figure 4 b cho thấy sự phân bố của các nguyên tố trong mẫu AgCu−SiO 2 . Sự phân bố của silicium và oxygen đồng đều trong hình ảnh. Bạc phân bố dày đặc hơn so với đồng, và các vị trí phân bố của chúng khác nhau. Điều đó cho thấy trong mẫu AgCu−SiO 2 , bạc có hàm lượng cao hơn nhiều so đồng. Bạc, đồng tồn tại ở các pha riêng biệt, phù hợp với kết quả XRD ( Figure 2 ). Những kết quả này chứng tỏ rằng mẫu AgCu−SiO 2 tồn tại ở dạng composite lưỡng kim. Bên cạnh đó, kết quả phân tích ICP-MS và AAS cho thấy, mẫu AgCu−SiO 2 chứa 28,14 ± 0,03% khối lượng nguyên tố bạc và 5,09 ± 0,11% nguyên tố đồng; trong khi đó mẫu Ag−SiO 2 chứa 30,08 ± 0,50% khối lượng nguyên tố bạc, và mẫu Cu−SiO 2 chứa 13,91 ± 0,97% khối lượng nguyên tố đồng.
Figure 2 . Giản đồ XRD của các mẫu Ag−SiO 2 , Cu−SiO 2 và AgCu−SiO 2 , kèm theo giản đồ XRD chuẩn của kim loại bạc và đồng.
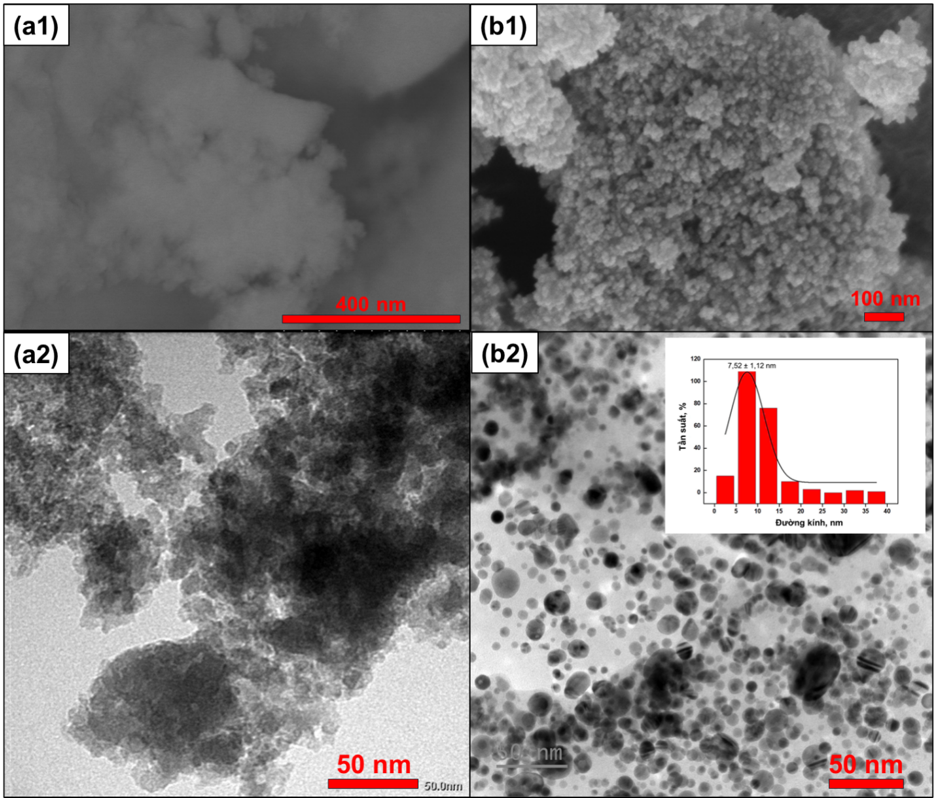
Hình thái của AgCu−SiO 2 được thể hiện thông qua kết quả hình ảnh SEM và TEM, được trình bày ở Figure 3 . Mẫu SiO 2 chứa các hạt tơi xốp và không có biên hạt rõ ràng ( Figure 3 a1, a2). Trong khi đó, mẫu AgCu−SiO 2 có nhiều hạt nhỏ từ vài nano mét đến vài chục nano mét với đường kính trung bình 7,52 ± 1,12 nm, phân bố dày đặc trên bề mặt vật liệu ( Figure 3 b1, b2). Kết quả SEM và kết quả XRD chứng tỏ trong AgCu−SiO 2 có các hạt nano kim loại đồng và bạc, được cố định trên bề mặt của SiO 2 .
Hoạt tính kháng nấm của vật liệu
Hoạt tính kháng nấm của vật liệu
Hoạt tính kháng nấm của vật liệu
Hoạt tính kháng nấm của vật liệu
KẾT LUẬN
Nanocomposite AgCu−SiO 2 được tổng hợp thành công bằng phương pháp khử hóa học xanh, kết hợp với sóng siêu âm cường độ cao. Các hạt nano kim loại với kích thước từ vài nano mét đến vài chục nm và kích thước hạt trung bình là 7,52 ± 1,12 nm được phân bố dày đặc trên bề mặt silica. Bên cạnh đó, AgCu−SiO 2 có khả năng ức chế hiệu quả sự phát triển của các nấm R. solani , F. oxysporum và P. catenulatum , gây bệnh lở cổ rễ cho cây cà chua. Nano đồng có ảnh hưởng mạnh hơn đến khả năng kháng nấm so với nano bạc đối với cả ba loại nấm, và các nấm R. solani và P. catenulatum rất mẫn cảm với vật liệu chứa nano đồng. Nấm R. solani không phát triển ở các nghiệm thức Cu−SiO 2 (125 ppm) và AgCu−SiO 2 (125 ppm), trong khi nấm này phát triển ở nghiệm thức Ag−SiO 2 (125 ppm) với đường kính 17,93 mm và phát triển đầy đĩa petri (80 mm) ở nghiệm thức đối chứng sau 72 giờ sau cấy. Đối với nấm F. oxysporum , các vật liệu Ag−SiO 2 và Cu−SiO 2 đạt hiệu lực ức chế cao nhất khoảng 80% ở nồng độ 125 ppm, còn AgCu−SiO 2 (125 ppm) đạt hiệu lực ức chế 100%, bằng với nghiệm thức thuốc hóa học Ridomil gold 68 WG (nồng độ khuyến cáo 3000 ppm). Các kết quả trên cho thấy sự kết hợp bạc và đồng trong nanocomposite AgCu−SiO 2 làm tăng cường hoạt tính kháng nấm, gây bệnh lở cổ rễ của cây cà chua.
DANH MỤC CÁC TỪ VIẾT TẮT
Ag NP: nano bạc
Cu NP: nano đồng
Si NP: nano silic
UV-Vis: hổ hấp thụ từ ngoại – khả kiến
XRD: Giản đồ nhiễu xạ tia X
ICP-MS: Phổ nguồn plasma cảm ứng cao tần kết nối khối phổ
AAS: Phổ hấp thụ nguyên tử
XUNG ĐỘT LỢI ÍCH
Các tác giả tuyên bố rằng không có xung đột lợi ích.
ĐÓNG GÓP CỦA CÁC TÁC GIẢ
Nghiên cứu này được thiết kế bởi Trần Công Khánh. Trần Quốc Vinh, Bùi Thị Thu Thảo, Trần Thị Huỳnh Như, Huỳnh Lê Nhựt Thủy, Triệu Huy Văn và Võ Thị Ngọc Hà thực nghiệm, thu thập số liệu và xử lý kết quả. Bản thảo được viết bởi Đặng Vinh Quang và Trần Công Khánh.
LỜI CẢM ƠN
Nghiên cứu được tài trợ bởi Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh (ĐHQG-HCM) trong khuôn khổ Đề tài mã số B2023-18-16.
References
- Burgess LW, Knight TE, Tesoriero L, Hiền PT. Cẩm nang chẩn đoán bệnh cây ở Việt Nam. Trung tâm Nghiên cứu Nông nghiệp Quốc tế Australia (ACIAR), 2009, 210. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Wang Y, Deng C, Rawat S, Cota-Ruiz K, Medina-Velo I, Gardea-Torresdey JL. Evaluation of the Effects of Nanomaterials on Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Responses: Underlining the Benefits of Nanotechnology for Agricultural Applications. ACS Agric Sci Technol [Internet]. 2021 Apr 19 [cited 2024 Dec 16];1(2):44–54. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Pham DC, Nguyen TH, Ngoc UTP, Le NTT, Tran TV, Nguyen DH. Preparation, Characterization and Antifungal Properties of Chitosan-Silver Nanoparticles Synergize Fungicide Against Pyricularia oryzae. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018 Aug 1;18(8):5299–305. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Vinh TQ, Thao BTT, Ha VTN, Quang DV, Khanh TC. Synthesis of copper/silica nanocomposites for application in preventing Ralstonia solanacearum bacteria causing the wilt disease. Science & Technology Development Journal: Natural Sciences [Internet]. 2024 Jun 30 [cited 2024 Dec 15];8(2):2947–55. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Hsieh JH, Yeh TH, Hung SY, Chang SY, Wu W, Li C. Antibacterial and tribological properties of TaN–Cu, TaN–Ag, and TaN–(Ag,Cu) nanocomposite thin films. Materials Research Bulletin [Internet]. 2012 Oct 1 [cited 2024 Dec 15];47(10):2999–3003. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Hengel IAJ van, Tierolf MW a. M, Valerio VPM, Minneboo M, Fluit AC, Fratila-Apachitei LE, et al. Self-defending additively manufactured bone implants bearing silver and copper nanoparticles. J Mater Chem B [Internet]. 2020 Feb 26 [cited 2024 Dec 15];8(8):1589–602. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Mureed S, Naz S, Haider A, Raza A, Ul-Hamid A, Haider J, et al. Development of Multi-concentration Cu:Ag Bimetallic Nanoparticles as a Promising Bactericidal for Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria as Evaluated with Molecular Docking Study. Nanoscale Res Lett [Internet]. 2021 May 22 [cited 2024 Dec 15];16(1):91. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Medina JC, Garcia-Perez VI, Zanella R. Metallic composites based on Ag, Cu, Au and Ag-Cu nanoparticles with distinctive bactericidal effect on varied species. Materials Today Communications [Internet]. 2021 Mar 1 [cited 2024 Dec 15];26:102182. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Cruces E, Arancibia-Miranda N, Manquián-Cerda K, Perreault F, Bolan N, Azócar MI, et al. Copper/Silver Bimetallic Nanoparticles Supported on Aluminosilicate Geomaterials as Antibacterial Agents. ACS Appl Nano Mater [Internet]. 2022 Jan 28 [cited 2024 Dec 15];5(1):1472–83. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Naaz H, Rawat K, Saffeullah P, Umar S. Silica nanoparticles synthesis and applications in agriculture for plant fertilization and protection: a review. Environ Chem Lett [Internet]. 2023 Feb 1 [cited 2025 Feb 21];21(1):539–59. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Cui J, Liu T, Li F, Yi J, Liu C, Yu H. Silica nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice cells: Mechanisms and size effects. Environ Pollut. 2017 Sep;228:363–9. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Tripathi DK, Singh S, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Dubey NK, Chauhan DK. Silicon nanoparticles more effectively alleviated UV-B stress than silicon in wheat (Triticum aestivum) seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2017 Jan;110:70–81. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Abdel-Haliem MEF, Hegazy HS, Hassan NS, Naguib DM. Effect of silica ions and nano silica on rice plants under salinity stress. Ecological Engineering [Internet]. 2017 Feb 1 [cited 2024 Dec 15];99:282–9. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Jullok N, Van Hooghten R, Luis P, Volodin A, Van Haesendonck C, Vermant J, et al. Effect of silica nanoparticles in mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation dehydration of acetic acid aqueous solution: plant-inspired dewatering systems. Journal of Cleaner Production [Internet]. 2016 Jan 20 [cited 2024 Dec 16];112:4879–89. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Janmohammadi M, Amanzadeh T, Sabaghnia N, Ion V. Effect of nano-silicon foliar application on safflower growth under organic and inorganic fertilizer regimes. Botanica Lithuanica [Internet]. 2016 Jun 1 [cited 2024 Dec 15];22(1):53–64. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Bui TTT, Tran VQ, Dang VQ, Nguyen TT, Vo TNH, Do DT, et al. Study of stability and antimicrobial activity of colloidal Ag/SiO2 nanocomposites. Adv Nat Sci: Nanosci Nanotechnol [Internet]. 2021 Jun [cited 2024 Dec 15];12(2):025010. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Liu P, Wang H, Li X, Rui M, Zeng H. Localized surface plasmon resonance of Cu nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid media. RSC Adv [Internet]. 2015 Sep 18 [cited 2024 Dec 15];5(97):79738–45. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Yan J, Zhang D, Zou G, Liu L, Zhou YN. Preparation of Oxidation-Resistant Ag-Cu Alloy Nanoparticles by Polyol Method for Electronic Packaging. J Electron Mater [Internet]. 2019 Feb 1 [cited 2024 Dec 15];48(2):1286–93. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Fan X, Yahia L, Sacher E. Antimicrobial Properties of the Ag, Cu Nanoparticle System. Biology (Basel) [Internet]. 2021 Feb 10 [cited 2024 Dec 15];10(2):137. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Aprilia S, Rosnelly CM, Zuhra, Fitriani F, Haffiz Akbar E, Raqib M, et al. Synthesis of amorphous silica from rice husk ash using the sol–gel method: Effect of alkaline and alkaline concentration. Materials Today: Proceedings [Internet]. 2023 Jan 1 [cited 2024 Dec 16];87:225–9. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Ngọc NTB, Châu NH, Tin TX, Nhất LM, Dung PT, Hường NTT, et al. Nghiên cứu hiệu quả của hạt nano bạc ức chế một số chủng nấm thực vật (Fusarium oxysporum, Colletotrichum, Rhizoctonia sonali và Corynespora cassiicola) TRONG PHÒNG THÍ NGHIỆM. Tạp chí Khoa học và Công nghệ Nông nghiệp Việt Nam. 2015;05(59):80–7. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Thirumoorthy G, Balasubramanian B, George JA, Nizam A, Nagella P, Srinatha N, et al. Phytofabricated bimetallic synthesis of silver-copper nanoparticles using Aerva lanata extract to evaluate their potential cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2024 Jan 13 [cited 2024 Dec 16];14(1):1270. . ;:. Google Scholar
- Hai NTT, Phuong TNM, Luong NV, Toan DK, Hoa TT, Thuy NTT. Synthesis and in vitro Antifungal Efficacy of Copper-silica Nanocomposites against Pathogenic Fungi of Rice. VNU Journal of Science: Natural Sciences and Technology [Internet]. 2020 Dec 22 [cited 2024 Dec 15];36(4). . ;:. Google Scholar
- El-Batal AI, Eid NA, Al-Habeeb RS, Al-Bishri WM, El-Sayyad GS, Badran AE. Promising antifungal behavior of biosynthesized bimetallic silver-copper oxide nanoparticles and Bacillus safensis against some strawberry rots. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology [Internet]. 2024 Sep 1 [cited 2025 Feb 21];133:102366. . ;:. Google Scholar
- El-Batal AI, Eid NA, Al-Habeeb RS, Al-Bishri WM, El-Sayyad GS, Badran AE. Promising antifungal behavior of biosynthesized bimetallic silver-copper oxide nanoparticles and Bacillus safensis against some strawberry rots. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology [Internet]. 2024 Sep 1 [cited 2024 Dec 15];133:102366. . ;:. Google Scholar

 Open Access
Open Access